RAID LEVELS
RAID LEVEL 3: RAID Level 3 Storage | RAID 3 Advantages and Disadvantages
The data block is subdivided ("striped") and written on the data disks. Stripe parity is generated on Writes, recorded on the parity disk and checked on Reads.
RAID Level 3 storage requires a minimum of 3 drives to implement
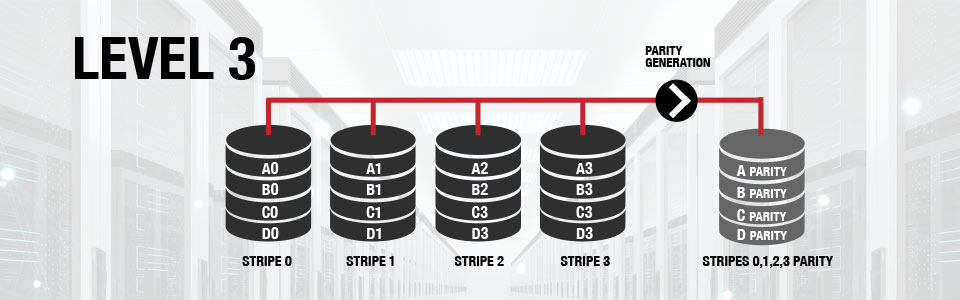
Characteristics & Advantages
- Very high Read data transfer rate
- Very high Write data transfer rate
- Disk failure has an insignificant impact on throughput
- Low ratio of ECC (Parity) disks to data disks means high efficiency
Disadvantages
- Transaction rate equal to that of a single disk drive at best (if spindles are synchronized)
- Controller design is fairly complex
- Very difficult and resource intensive to do as a "software" RAID
Recommended Applications
- Video Production and live streaming
- Image Editing
- Video Editing
- Prepress Applications
- Any application requiring high throughput




